ABOUT PRESCRIPTION RESTRICTIONS
Administrators can impose or lift various levels of prescription restrictions on active Prescribers. This prevents them from prescribing specific medication for a stated period of time.
Orders to impose or lift restrictions must come from the hospital’s Department Head or higher. This process requires official hospital paperwork, an explanation, and the specified duration of any restrictions. The Prescriber receives a notification about any changes in prescription restrictions the next time they open the application.
You can view the details of a Prescriber’s restrictions in their profile.

RESTRICTION CATEGORIES
The following are the available restriction categories for this feature.
NO RESTRICTIONS
The Prescriber has no medication restrictions for prescriptions. However, prescribed medication must align with the patient’s current diagnosis saved in the Daley Dose database.
Note: The application sets this option as the default for newly added prescription accounts.
STRONG NARCOTICS LOCK
The Prescriber cannot add Schedule II medication to their Daley Dose prescriptions, regardless of whether the patient profile permits its administration.
HIGH RISK SUBSTANCES LOCK
The Prescriber cannot add Schedule II or Schedule III medication to their Daley Dose prescriptions, regardless of whether the patient profile permits its administration.
CONTROLLED PRESCRIPTION LOCK
The Prescriber cannot add Schedule II, Schedule III, or Schedule IV medication to their Daley Dose prescriptions.
MAXIMUM RESTRICTIONS
The Prescriber can add only Schedule V and over‑the‑counter (OTC) medication to their Daley Dose prescriptions.
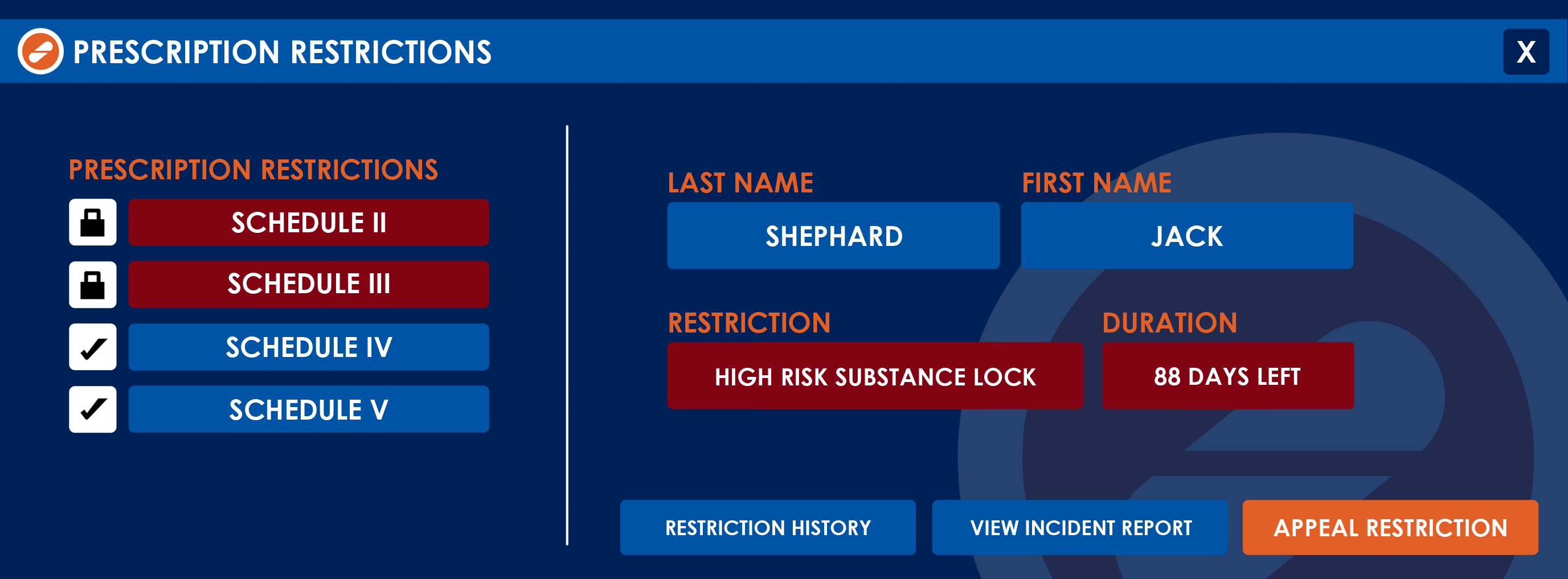
DRUG CLASSIFICATIONS
The following are drug classifications that can be restricted by this feature.
SCHEDULE TWO
- Drugs with a high potential for abuse, with use potentially leading to severe psychological or physical dependence. Considered dangerous.
- Examples: Oxycodone, Hydromorphone, Methadone, Fentanyl, Morphine, Amphetamine (Adderall), Methamphetamine, Methylphenidate (Ritalin)
SCHEDULE THREE
- Drugs with a moderate to low potential for physical and psychological dependence. Abuse potential is less than Class I or II but still significant.
- Examples: Anabolic steroids, Testosterone, Ketamine, Buprenorphine, Codeine (when combined with acetaminophen)
SCHEDULE FOUR
- Drugs with a low potential for abuse and low risk of dependence compared to Class III.
- Examples: Alprazolam (Xanax), Diazepam (Valium), Lorazepam (Ativan), Zolpidem (Ambien), Tramadol
SCHEDULE FIVE
- Drugs with the lowest potential for abuse. Often preparations containing limited quantities of certain narcotics.
- Examples: Cough preparations with less than 200 mg of codeine per 100 ml (Robitussin AC), Ezogabine, Pregabalin (Lyrica), Lomotil
OVER-THE-COUNTER (OTC)
- Medications available without a prescription. Generally recognized as safe and effective for self-use when taken as directed. Lowest risk of abuse or dependence.
- Examples: Acetaminophen (Tylenol), Ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin), Diphenhydramine (Benadryl), Loratadine (Claritin), Antacids (Tums, Rolaids)